Cyber-Informed Engineering
Managing Cyber Risk from Concept to Operation
Cyber-Informed Engineering (CIE) builds tools for high-level implementation into curriculum, design standards, certification and curriculum accreditation.
CIE deepens the cybersecurity protections for critical infrastructure by providing guidance to allow defenses from cyberattack to be engineered in from the early design life cycle of infrastructure systems. It provides additional mechanisms to mitigate the worst consequences of cyberattack and leverages digitally based defenses prioritized by the consequences of cyberattack to the process and infrastructure of the critical infrastructure asset owner. CIE provides a framework for a change in philosophy and engineering practices for system design to proactively secure existing infrastructure and build novel future technology designed to withstand the modern and future cyber-adversary.
The Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER) sponsors INL CIE initiatives and coordinates the CIE program that includes INL; the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and industry, academic, and other partners in support of the Department of Energy’s National Cyber-informed Engineering Strategy, and the National Cybersecurity Strategy.
Managing Cyber Risk from Concept to Operation
Cyber-Informed Engineering (CIE) is a strategic initiative championed by Idaho National Laboratory (INL) to integrate cybersecurity into engineering practices for critical infrastructure. INL leads in implementing the national strategy by developing engineering tools, standards, and educational resources that prioritize cybersecurity in infrastructure design and operation.
INL’s key contributions to CIE include:
- A 200-member CIE Community of Practice for collaboration and knowledge exchange.
- A CIE Implementation Guide and Resource Library to facilitate the adoption of CIE practices.
- Partnerships with academic and industry stakeholders to incorporate CIE into engineering programs and infrastructure projects.
INL’s efforts ensure that infrastructure is designed with inherent defenses against cyber threats, enhancing the resilience of energy systems against potential attacks.
The Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER) sponsors INL CIE initiatives and coordinates the CIE program that includes INL; the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and industry, academic, and other partners in support of the Department of Energy’s National Cyber-informed Engineering Strategy, and the National Cybersecurity Strategy.
CIE Development Tools
Resource Library
Implementation Guide
Analysis Tool
Microgrid Analysis Tool
National Cyber-Informed Engineering Strategy
The U.S. Department of Energy’s National CIE Strategy guides energy sector efforts to incorporate cybersecurity practices into the design life cycle of engineered systems to reduce cyber risk.
National Cybersecurity Strategy
The DOE’s National CIE Strategy, highlighted in the March 2023 National Cyber Strategy, ensures proactive cybersecurity for our clean energy future.
CIE is integral to the National Cybersecurity Strategy Implementation Plan. In section 4.4.3, the DOE announces an initiative to build training, tools, and support for engineers and technicians using CIE principles.
Strategy for Cyber-Physical Resilience: Fortifying Our Critical Infrastructure for a Digital World
The President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST) is a federal advisory committee appointed by the president to provide science and technology advice. Comprising 28 distinguished leaders, PCAST advises on policies related to the economy, education, energy, environment, public health, security, racial equity, and more.
National Cyber Workforce and Education Strategy
All participants in software development—from business leaders to software developers and product managers—must manage the security and privacy implications of their work. The Department of Energy’s 2022 National Cyber-Informed Engineering Strategy serves as a model, emphasizing the integration of cybersecurity principles from the earliest to the final stages of engineering.
COME JOIN THE CIE COMMUNITY OF PRACTICE
Second Wednesday of January, April, July, and October 9 a.m. MT / 11 a.m. ET quarterly
Standards Working Group
First Wednesday at 9 a.m. MT / 11 a.m. ET monthly
Education Working Group
Third Wednesday at 9 a.m. MT / 11 a.m. ET monthly
Development Working Group
Fourth Wednesday at 9 a.m. MT / 11 a.m. ET monthly
CIE Highlights
DOE adds two new resources to advance awareness, implementation of CIE in energy sector
Is the U.S. Government’s Cyber Informed Engineering Implementation Guide the long-awaited breakthrough in CIP?
Meaningful strides possible with CIE and CCE methodologies across industrial cybersecurity landscape
CIE and CCE methodologies can deliver engineered industrial systems for holistic system cybersecurity
CIE Workbooks
CIE Is the WHAT and CCE Is a HOW
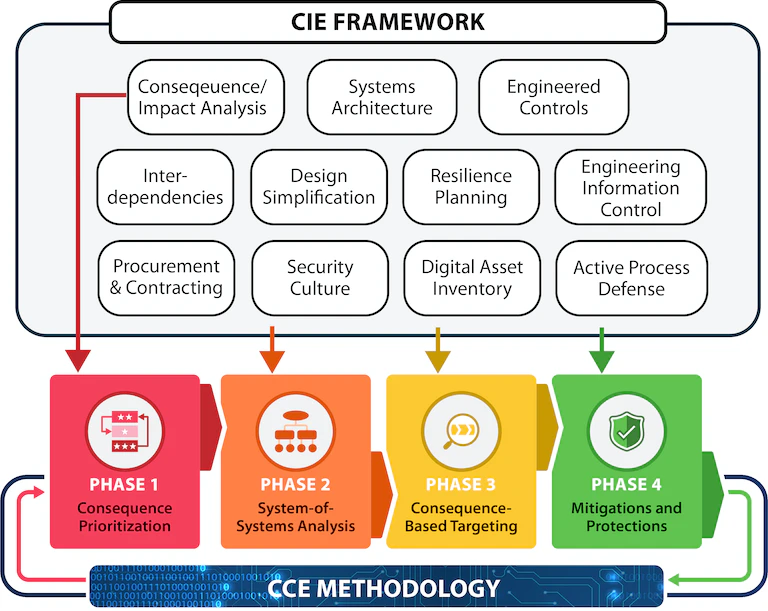
The Department of Energy and INL have developed a framework to guide the application of cybersecurity principles across the engineering design life cycle. The Cyber-Informed Engineering (CIE) framework and body of knowledge drives the inclusion of cybersecurity as a foundational element of risk management for engineering of functions aided by digital technology. Consequence-Driven Cyber-Informed Engineering (CCE) is a rigorous process for applying CIE’s core principles to a specific organization, facility, or mission by identifying the most critical functions, and the methods and means an adversary would likely use to manipulate or compromise them, to determine the most effective means of removing or mitigating those risks.
CIE emphasizes “engineering out” potential risk in key areas, as well as ensuring resiliency and response maturity within the design of the engineered system. The following CIE framework shows some of the key focus areas and how they relate to the CCE methodology. CCE walks an organization through core components of CIE in CCE’s four-phase process to evaluate and remove or mitigate weaknesses in their critical functions.
CIE Presentations
What is Cyber-Informed Engineering?
Hosted by Idaho National Laboratory and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, this webinar offers a CIE primer for energy companies, engineering firms, suppliers and manufactures, researchers, standards organizations, and government partners.
U.S. Senate Committee: Testimony
Securing U.S. critical water infrastructure in the energy sector requires preventing cyber threats by enhancing engineering and removing vulnerabilities. As hydropower systems modernize, increased support for threat identification and mitigation is essential. Cyber-informed engineering enables INL to ensure resilience against nation-state cyberattacks.
CIE Practitioner Workshop Videos
Check out our CIE Practitioner Workshop video playlist for expert insights on cybersecurity design. Learn how to apply Cyber-Informed Engineering principles to enhance the security and resilience of critical infrastructure.
Auburn University Hosts Energy Security: Cyber-informed Engineering
INL’s Zach Tudor and other industry leaders discussed this CIE strategy, why it matters and how you can help with implementation.
Fermilab Colloquium 2016
Cyber-informed engineering is a body of knowledge and methodologies to characterize and mitigate risks presented by the introduction of digital technology in this formerly analog environment. It is focused on applying traditional engineering techniques informed by an awareness of cybersecurity threat and mitigation methods. This talk described how managers and engineers can participate in mitigating cybersecurity risk in engineering projects throughout the design and installation life cycle.
Resilience Week CIE Presentation
Oct. 19-23, 2020
By Virginia Wright
Better Securing the Now and the Next: Applying Engineering Base Principles to Achieve Demonstrably Better Cybersecurity.
Presented by Andy Bochman and Virginia Wright
CIE – Domestic Nuclear Cyber
An introduction of CIE and how it pertains to nuclear energy and cybersecurity.
By Virginia Wright