National & Homeland Security Testing Facilities
The National and Homeland Security Testing Facilities are singularly positioned to support a wide variety of full-scale and practical testing opportunities for the Department of Energy, Department of Defense, National Nuclear Security Administration, Department of Homeland Security, and other federal and industrial collaborators. INL has a campus in Idaho Falls and an isolated 890-square mile desert Site located about 45 miles west of Idaho Falls. The Site’s unparalleled geography includes several dedicated test ranges and available airspace that allows research to be conducted safely and securely.
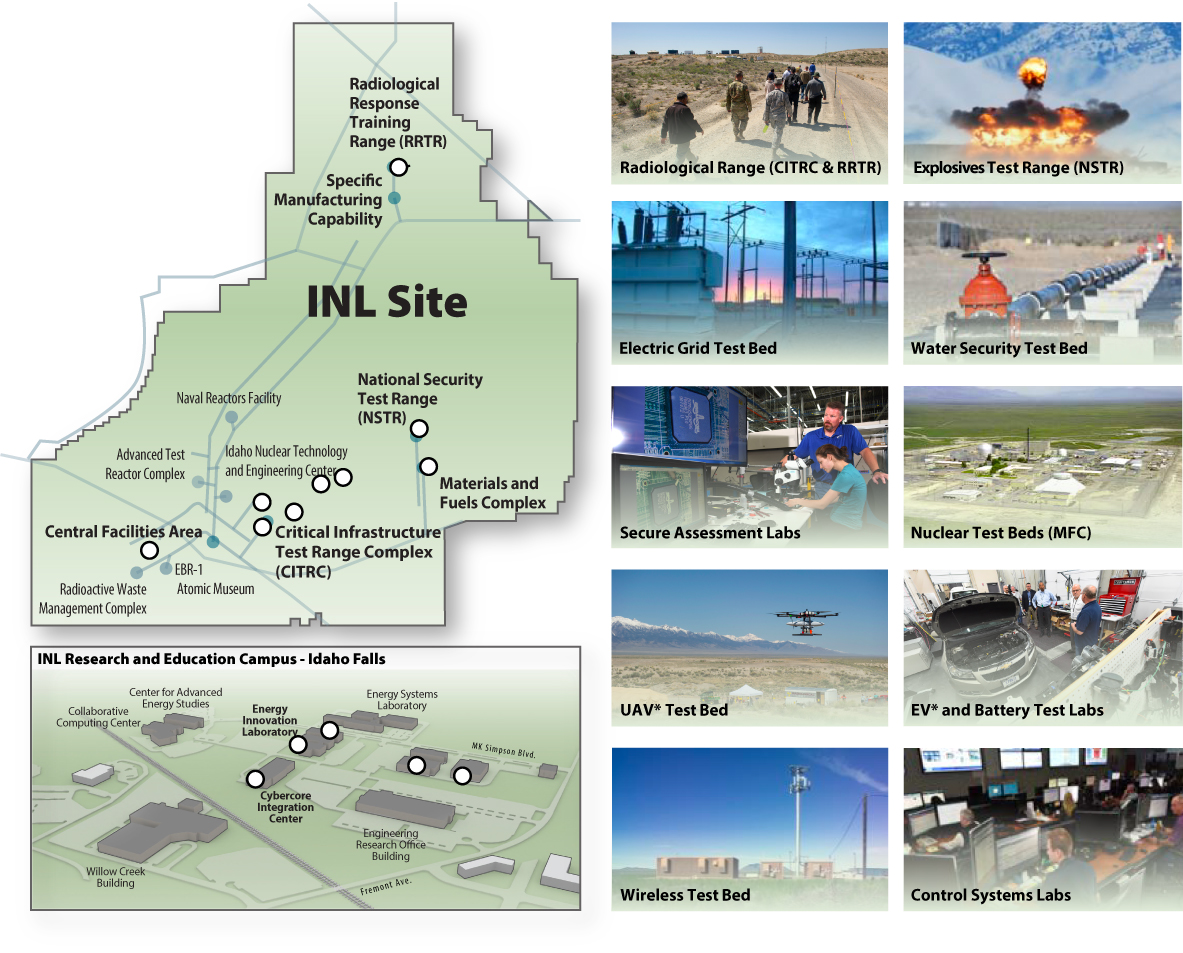
Radiological Range
The laboratory’s 890-squaremile site can be used for largescale interagency technology 13-GA50222-03 and capability demonstrations. Students also have access to nuclear facilities including operating reactors, hot cells, and analytical laboratories inside a controlled location that provides a safe and secure environment for training.
- INL has conducted RDD and WMD classroom and field training since 2002.
- Participants have controlled access to live radioactive materials including sealed sources, fissile materials, and spent nuclear fuels.
- INL’s 890-square-mile site, nuclear infrastructure, and staff expertise are ideal for conducting detection, identification, measurement, and recovery exercises.
- The laboratory has provided source material and expertise to agencies wishing to conduct training at their facilities.
- INL’s site has been utilized for several radiological joint capability and technology demonstrations.
Explosives Test Range
The complex consists of eight indoor and outdoor ranges, and tactical training facilities located on 330 acres of isolated, desert-type terrain. The facilities support research and development testing and training and testing of handguns, rifles and heavy weapons such as machine guns, precision rifles, grenade launchers and shoulder-fired, anti-armor weapons. Explosive training and testing, including breaching, is also conducted.
National Security Test Range provides access to capabilities to understand and mitigate emerging challenges being faced on the battlefield.
- 8.7 km range fan
- Classified testing capability
- Tactical breaching training
- Classified networking
- Dynamic testing experience
Electric Grid Test Bed
INL operates its own electrical power transmission and distribution system, 24/7. The grid, which is linked with state-of-the-art SCADA, communications and cyber testing capabilities, is operated under a full range of climatic conditions (temperature, wind, snow, ice, ozone). We can safely isolate sections of the grid and associated infrastructure to conduct full-scale testing of technology, components, systems and processes.
This functioning power grid consists of 61 miles of 138 kV transmission loop distribution that feeds power to the INL and allow our expert staff to configure numerous network topologies to meet any customer’s needs. Within the loop there are multiple feeders, transformers, and seven independent substations. These resources allow us to bring testing out of the theoretical, and into the real world.
Water test bed
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established the Water Security Test Bed (WSTB) at INL to inform responses to disasters that interrupt domestic water supplies. About 450 feet of eight-inch piping is assembled above ground to simulate a full-scale distribution system. Researchers are able to easily modify the system and contain any nefarious agents that may be injected into the pipe as part of an experiment. A typical experiment involves injecting a biological or chemical agent followed by flushing, chlorination, or other decontamination methods.
Secure Assessment Lab
As a world leader in control systems cybersecurity, INL has more than 100,000 square feet of laboratory and electronics testing space for analyzing and testing operational technology such as industrial control systems and other relevant technology including programmable logic controllers, remote terminal units, digital relays and energy management systems. These labs are enhanced by employees with specialized expertise in operational technology cybersecurity, power systems engineering and vulnerability analysis. The lab’s control systems test beds can be connected directly to INL’s grid, creating a full-scale test and evaluation environment.
Nuclear Test Beds
INL’s radiological facilities and an expansive site provide an unprecedented environment for research, demonstration and realistic training exercises aligned with today’s national security challenges.
- Access to various forms of nuclear materials
- Analytical laboratories
- Authorized environmental and safety permits
- Expertise to support aerial measurements and ground sampling
- Forensic and dispersion training facilities
- Specifically suited for testing nuclear technology
- Supports large scale nuclear technology demonstration
- Assists in the deployment of nuclear technologies
UAV Test Bed
With its access-controlled boundary, high-desert terrain and sparse population, INL’s desert site is in a unique position to offer unmanned aerial vehicle and unmanned ground vehicle collaborative operational testing and demonstration. INL’s UAS program focuses on unique applications and missions for a wide variety of customers looking for affordable, field-deployable airframe technologies with meaningful payload and endurance. The lab’s UAS training is designed to ensure that unmanned aerial vehicles are used properly throughout the Department of Energy and its National Nuclear Security Administration. The range also supports implementation of new legislation regarding protection of critical infrastructure.
EV Test Labs
As a world leader in control systems cybersecurity, INL has more than 100,000 square feet of laboratory and electronics testing space for analyzing and testing operational technology such as industrial control systems and other relevant technology including programmable logic controllers, remote terminal units, digital relays and energy management systems. These labs are enhanced by employees with specialized expertise in operational technology cybersecurity, power systems engineering and vulnerability analysis. The lab’s control systems test beds can be connected directly to INL’s grid, creating a full-scale test and evaluation environment.
Wireless Test Bed
INL offers large-scale, end-to-end testing emerging cellular, land mobile radios, wireless local area network and backhaul (microwave, FSO, satellite) systems to industry and government. The laboratory is authorized by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) to operate as an experimental radio station.
As a result, INL can test communications systems with a view toward science or technology.
With its cell tower infrastructure, low RF noise, and access to INL’s experienced telecommunications design staff and test engineers, customers can test in an isolated environment without public beta test risks or impact to critical or emergency infrastructures.
- 170 miles of fiber - OC-3, OC-12 fiber links over SONET/ATM backbone.
- 2-way radio systems, cell phones, and hard-wired systems.
- intranet systems, intrusion detection, firewall, and secure communications.
Control Systems Labs
As a world leader in control systems cybersecurity, INL has more than 100,000 square feet of laboratory and electronics testing space for analyzing and testing operational technology such as industrial control systems and other relevant technology including programmable logic controllers, remote terminal units, digital relays and energy management systems. These labs are enhanced by employees with specialized expertise in operational technology cybersecurity, power systems engineering and vulnerability analysis. The lab’s control systems test beds can be connected directly to INL’s grid, creating a full-scale test and evaluation environment.
Leading Capabilities
- Several firing ranges and a blast ceiling of 20,000 pounds
- Over 60 miles of 138 kilovolt lines, multiple substations and power grids
- Cellular, microwave, satellite and fiber-optic backhaul wireless communication systems
- Over 100,000 square feet of cybersecurity labs, collaborative spaces and secure meeting spaces
- Municipal water system with pressurized pipelines, household systems and automated controls
- Over 3,000 square miles of Federal Aviation Administration Certificate of Authorization airspace with a 1,000-foot unmanned aerial systems runway
- Access to the world-leading Advanced Test Reactor and large nuclear material and post-irradiation examination hot cells