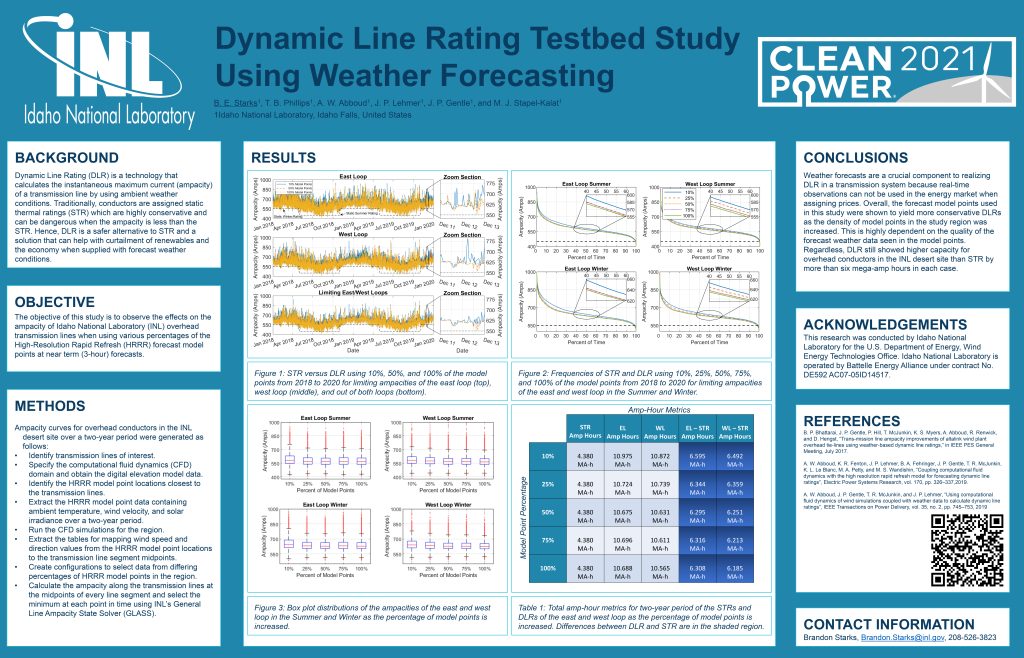
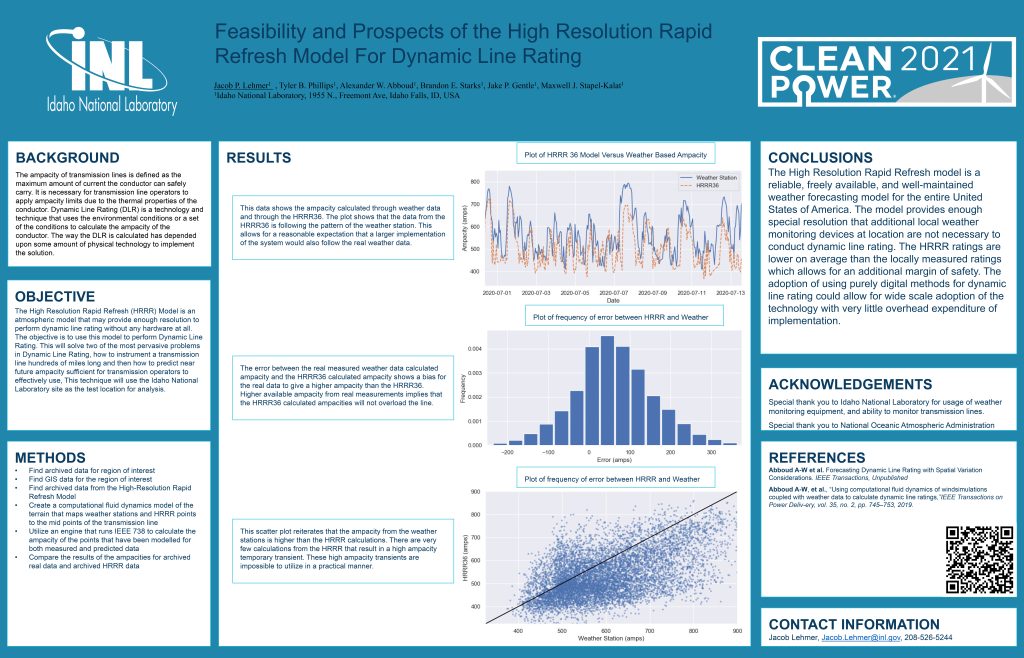
Dynamic Line Rating
Improving Energy Distribution Solutions
Grid transmission lines are given static ratings based on maximum ampacity and temperature limits. The weather conditions used by regulators in these methods are typically constant values year-round or with seasonal patterns and are set using conservative assumptions for the conditions. By not accounting for additional cooling during periods of high wind or low ambient temperature, there is likely unused head room on many overhead transmission lines.
What is a Dynamic Line Rating?
Dynamic Line Rating (DLR) is a changing transmission line rating based on local conditions rather than a static rating assumption and provides additional ampacity capacity to a transmission line. The U.S. Department of Energy has identified DLR as a transmission and distribution infrastructure solution to defer upgrades, support line outages and increase yields of distributed power. DLR is one of many solutions known as Grid Enhancing Technologies. Idaho National Laboratory is leading research and analysis on industry hardware and software DLR solutions. The conservative nature of transmission line standards and the regional transmission operators can be hard to adjust, so research showing the benefits of DLR is important to prove the benefits of the method.
How Does DLR work?
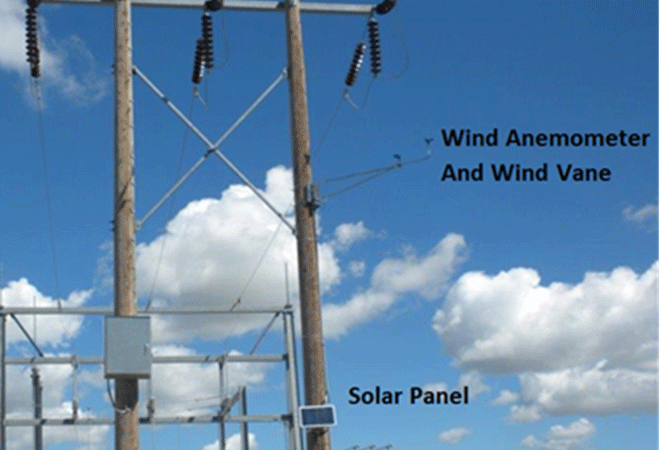
The ampacity of transmission lines is defined as the maximum amount of current the conductor can safely carry. Transmission line operators must apply ampacity limits due to the thermal properties of the conductor. Dynamic Line Rating (DLR) is a technology and technique that uses the environmental conditions or a set of the conditions to calculate the ampacity of the conductor. The way DLR is calculated has depended on some amount of physical technology to implement the solution.
Technical Article and Papers
Electric Power Systems Research, 170, 326-337 (2019)
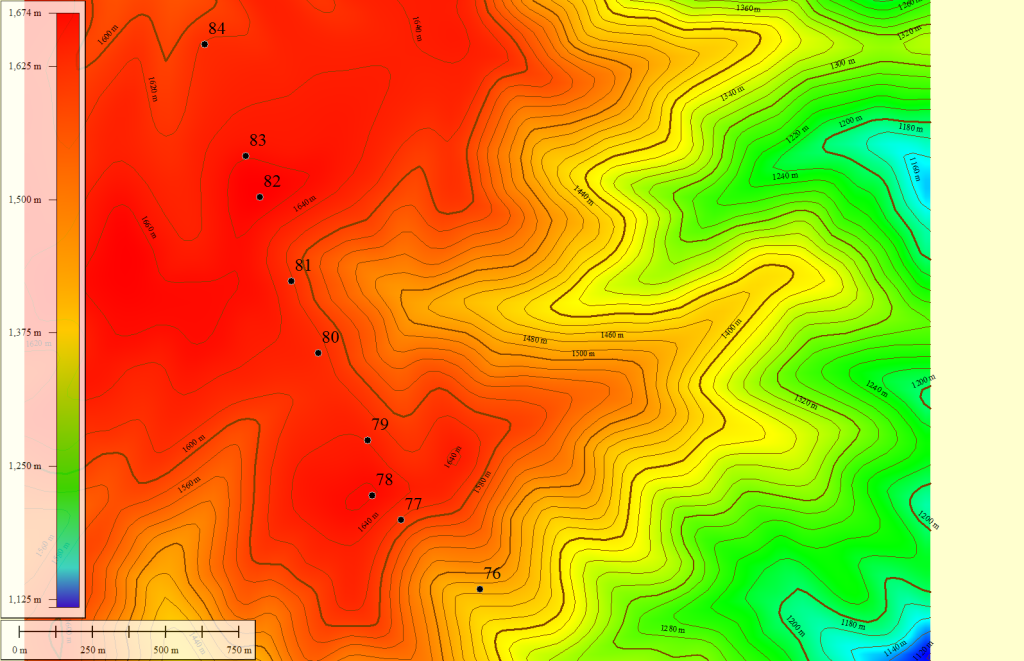
This study looks at forecasted dynamic line ratings in southern Idaho by using data from the high resolution rapid-refresh (HRRR) model for forecasted weather conditions.
IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 35(2), 745-753 (2019)
Dynamic line rating is a technology that allows for the rating of electrical conductors to be calculated based on local weather conditions rather than using “worst-case” assumptions of weather conditions.
IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 33(4), 1853-1863 (2018)
Most of the existing overhead transmission lines (TLs) are assigned a static rating by considering the conservative environmental conditions (e.g., high ambient temperature and low wind speed).
IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 34(6), 2100-2109 (2019)
Power flow, on both AC and DC overhead transmission lines, is limited to keep the conductor temperature below a maximum (TC
Study of Concurrent Cooling Effects for a Proposed Wind Farm (2021)
A report for the DOE Wind Energy Technology Office on the cost reducing outcomes of maximum wind farm power output coupled with additional convective cooling on the gen tie-line.
Grid Enhancing Technology Fact Sheets
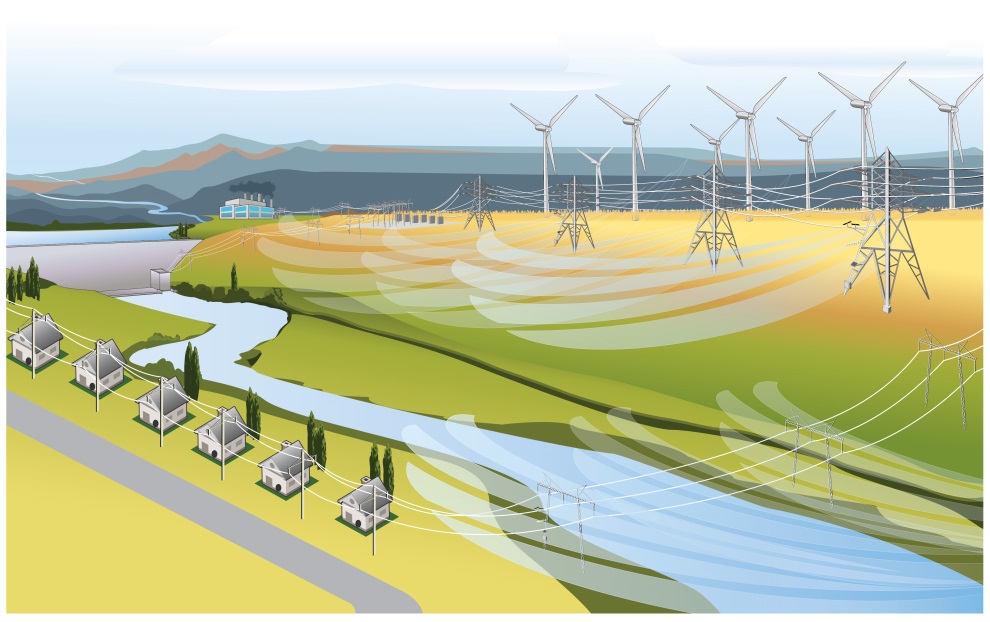

Dynamic Line Rating Overview
The U.S. electrical grid includes about 7,000 operational power plants that send electricity over 642,000 miles of high-voltage transmission lines and 6.3 million miles of distribution lines.

Transmission Line Modeling Tool Suite
The more electric current an electric line carries, the hotter it gets. After a certain point, a line operator cannot add additional current without overheating and damaging the line.

A Novel Wind Atlas Modeling Method
Almost every country has created wind resource maps to find potential windy places suitable for building new wind plants.

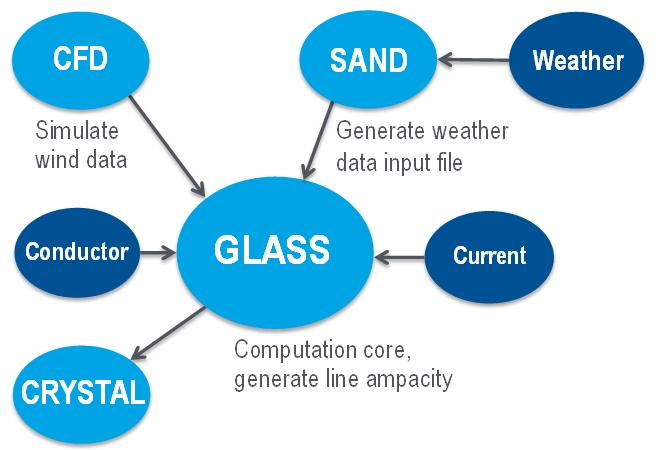
General Line Ampacity State Solver (GLASS)
Wind power researchers at Idaho National Laboratory believe moving more electricity through existing transmission lines is both possible and practical.

Safe Integration of New Grid Technologies
Utility operators have a massive amount of information to monitor in a control room.
Conferences and Presentations
Computerized Wind Farm Generation … Footprint Routing and Subsequent DLR
Transmission lines are the backbone of the U.S. electrical grid. Due to increased penetration of renewable resources, there is an increasing need to connect the often remote resources to existing transmission line infrastructure. To view presentation, click here.
Using Dynamic Line Ratings for Wind Farm Gen-Tie Line Considerations
IEEE/CIGRE standards provide a base for overhead transmission line ratings.
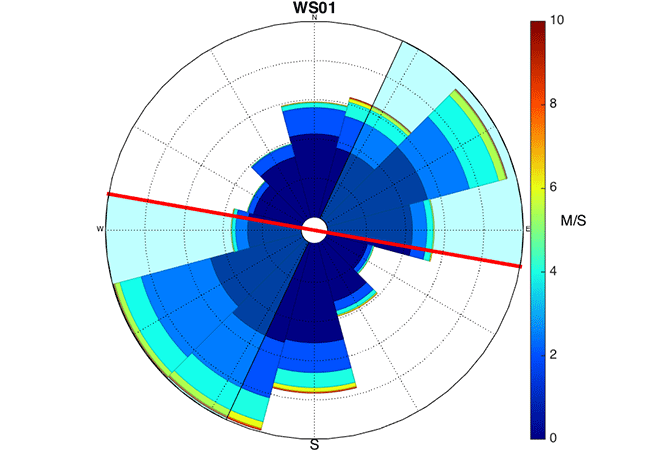
- Measuring many types of sensors could provide more capacity as a time varying capability.
- Wide Area Weather-based DLR can provide a calculation of the moment-to-moment steady-state rating.
Forecasting Dynamic Line Rating with Spatial Variation Considerations
Dynamic Line Rating is a technology that allows the ampacity of an electrical conductor to be calculated using real-time or forecasted weather conditions. To view presentation, click here.
Sensitivity Effects of High Temperature Overhead Conductors to Line Rating Variables
For traditional overhead transmission lines, the maximum allowable conductor operating temperature on ASCR, AAC or AAAC lines for determining the static line ratings can be quite low, typically well under 100 Celsius. At these low temperatures, the primary driver for determining static line ratings are assumptions made about the wind speed and direction and the ambient temperature.