Consequence-Driven Cyber-Informed Engineering
Safeguarding Critical Operations
Consequence-driven Cyber-Informed Engineering (CCE) is a methodology focused on securing the nation’s critical infrastructure systems. Developed at Idaho National Laboratory, CCE begins with the assumption that if a critical infrastructure system is targeted by a skilled and determined adversary, the targeted network can and will be penetrated. This “think like the adversary” approach provides critical infrastructure owners and operators a four-phase process for safeguarding their critical operations.
Methodology and Four-Phase Process
CCE provides a four-phase process for safeguarding critical infrastructure operations. The following graphic and animation provide more information for each of the four phases of the CCE Methodology.
CCE Process
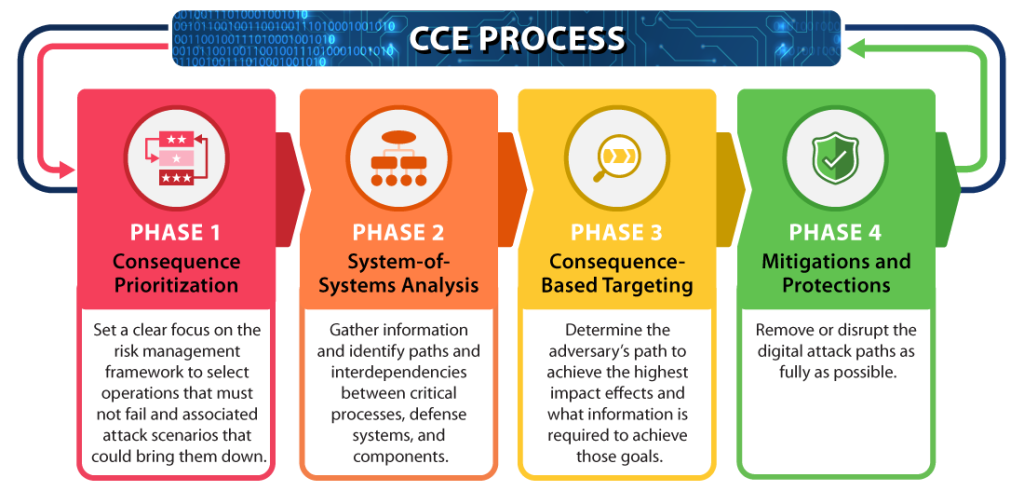
Animated CCE Kill Chain Workflow
Engagements and Training Opportunities
ACCELERATE Training
Course Description: ACCELERATE Training provides critical infrastructure companies with a self-guided approach to conducting their own CCE effort. The course is two days (16 hours) and includes CCE methodology plus a detailed guide and templates participants can use to facilitate a CCE effort within their organization. The course offers continuing educations units/credits. >>MORE INFO
Registration: FREE. Registrants are responsible for travel expenses (flight, hotel and meals).
For registration related questions, email: [email protected]
Other Training Opportunities
INL and DOE-supported CCE Engagement (Tier 1) – Specific engineering solutions — not just cyber controls — to design out cyber risk from critical operations.
Self-Driven CCE Engagement (Tier 2) – In-depth, team-based training for Tier 1 individuals
Workforce Development – In-depth, team-based training for select individuals who will help Tier 1 partners execute a CCE engagement.
CCE Licensed Industry Partners

Opswright
Read More

Sentar Company
Read More

West Yost Associates
Read More

CI-Discern
Read More

Advanced Technologies & Laboratories
Read More

1898 and Company
Read More

Black & Veatch Management Consulting
Read More

Mission Secure
Read More

MAG Aerospace
Read More

QED Secure Solutions
Read More
Additional Resources
Papers and Publications
NIST: SP 800-82 Rev. 3 (DRAFT) Guide to Operational Technology (OT) Security
The draft of NIST’s revision for their Guide to OT Security, now open for comments, includes an appendix on OT security organizations, research and activities, including a section for “INL Cyber-Informed Engineering (CIE) and Consequence-Driven Cyber-Informed Engineering (CCE)”
The Department of Energy and Idaho National Laboratory have developed a framework to guide the application of cybersecurity principles across the engineering design life cycle. The CIE framework and body of knowledge drives the inclusion of cybersecurity as a foundational element of risk management for engineering functions aided by digital technology.
CCE is a rigorous process for applying CIE’s core principles to a specific organization, facility, or mission by identifying their most critical functions, and the methods, and means an adversary would likely use to manipulate or compromise those critical functions, then determine the most effective means of removing or mitigating those risks. CIE emphasizes “engineering out” potential risk in key areas, as well as ensuring resiliency and response maturity within the design of the engineered system.
The following CIE framework shows some of the key focus areas and how they relate to the CCE methodology. CCE walks an organization through core components of CIE in CCE’s four-phase process to evaluate and remove or mitigate weaknesses in their critical functions.
Countering Cyber Sabotage Book

By Andrew Bochman and Sarah Freeman
January 2021
Countering Cyber Sabotage: Introducing Consequence-Driven, Cyber-Informed Engineering (CCE): This new methodology helps critical infrastructure owners, operators and their security practitioners make demonstrable improvements in securing their most important functions and processes.
Current best practice approaches to cyber defense to stop targeted attackers from creating potentially catastrophic results. The most pressing threat is cyber-enabled sabotage, and CCE begins with the assumption that well-resourced, adaptive adversaries are already in and have been for some time, undetected and perhaps undetectable.
The End of Cybersecurity

No amount of investment in digital defenses can protect critical systems from hackers. It’s time for a new strategy.
Harvard Business Review
By Andy Bochman
May 31, 2018
CCE Concept Paper

INL Mission Support Center Concept Paper
October 2016
CCE participants are encouraged to work collaboratively with each other and with key U.S. Government (USG) contributors to establish a coalition, maximizing the positive effect of lessons-learned and further contributing to the protection of critical infrastructure and other national assets.
Cyber Threat and Vulnerability Analysis of the U.S. Electric Sector

INL Mission Support Center Analysis Report
August 2016
This paper seeks to illustrate the current cyber-physical landscape of the U.S. electric sector in the context of its vulnerabilities to cyberattacks, the likelihood of cyberattacks, and the impacts cyber events and threat actors can achieve on the power grid. This paper also highlights utility perspectives, perceived challenges and requests for assistance in addressing cyber threats to the electric sector.
The Need for Cyber-informed Engineering Expertise for Nuclear Research Reactors

International Conference on Research Reactors: Safe Management and Effective Utilization
December 2015
This paper examines the need for Cyber-Informed Engineering practices that encompass the entire engineering life cycle. Cyber-Informed Engineering, as referenced in this paper, is the inclusion of cybersecurity into the engineering process. This paper addresses several attributes of this process and the long-term goal of developing additional cyber-safety basis analysis and trust principles. With a culture of free information-sharing exchanges, and potentially a lack of security expertise, new risk analysis and design methodologies must be developed to address this rapidly evolving (cyber) threatscape.
Presentations
2022 National ResilienceEXCH (Exchange) Summit - CCE Virtual event, January 27, 2021
MRO Power Meeting - Intro to CCE
RSA Conference 2019
S4 Conference 2019
Contact Information
Michelle Farrell
For more information contact: [email protected]