Anyone who has flown on a commercial flight, crossed an international border, visited a government building or attended a concert knows you’re not getting inside until you pass the security guards.
Placing guards outside the gates is a centuries-old defense strategy used to protect people, places and things from those who seek to do harm.
Like those guards, Idaho National Laboratory’s newest network anomaly detection technology —VigilantShield — is designed to keep viruses, malware and other malicious software from invading critical communication networks.
VigilantShield isn’t the first product in the market to fight against cyber threats, said INL researcher Matt Anderson. However, VigilantShield is the first to fight threats at the network level by using machine learning to sequester malicious network packets — digital containers filled with data — before they reach their intended destination, such as a cell phone or laptop. The ability to capture and sequester malicious data in transit opens a new front in the cyber battlefield.

“The conventional cybersecurity viewpoint is to just secure the end-point system rather than sequestering malicious software in the network while still in flight,” Anderson said. “Cyber criminals can send malware across networks with near impunity since the network packets aren’t being scanned, leaving the end-point systems to defend themselves. VigilantShield aims to defend against malicious behavior at the network level rather than at the end-point system.”
How does VigilantShield work?
VigilantShield examines cyber data packets on a network in real-time, efficiently identifying and stopping anomalous or malicious packets almost instantaneously — roughly 300 microseconds — before they can move through the network. VigilantShield captures these packet anomalies without disrupting network flow.
The technology works like a border crossing where thousands of vehicles pass through the border check every millisecond, Anderson said. Because of its speed, VigilantShield can scan each vehicle, pulling aside suspicious cars without interrupting the flow of traffic.

This quick and efficient process is important to network managers because it takes only moments for malicious packets to cause harm down the road.
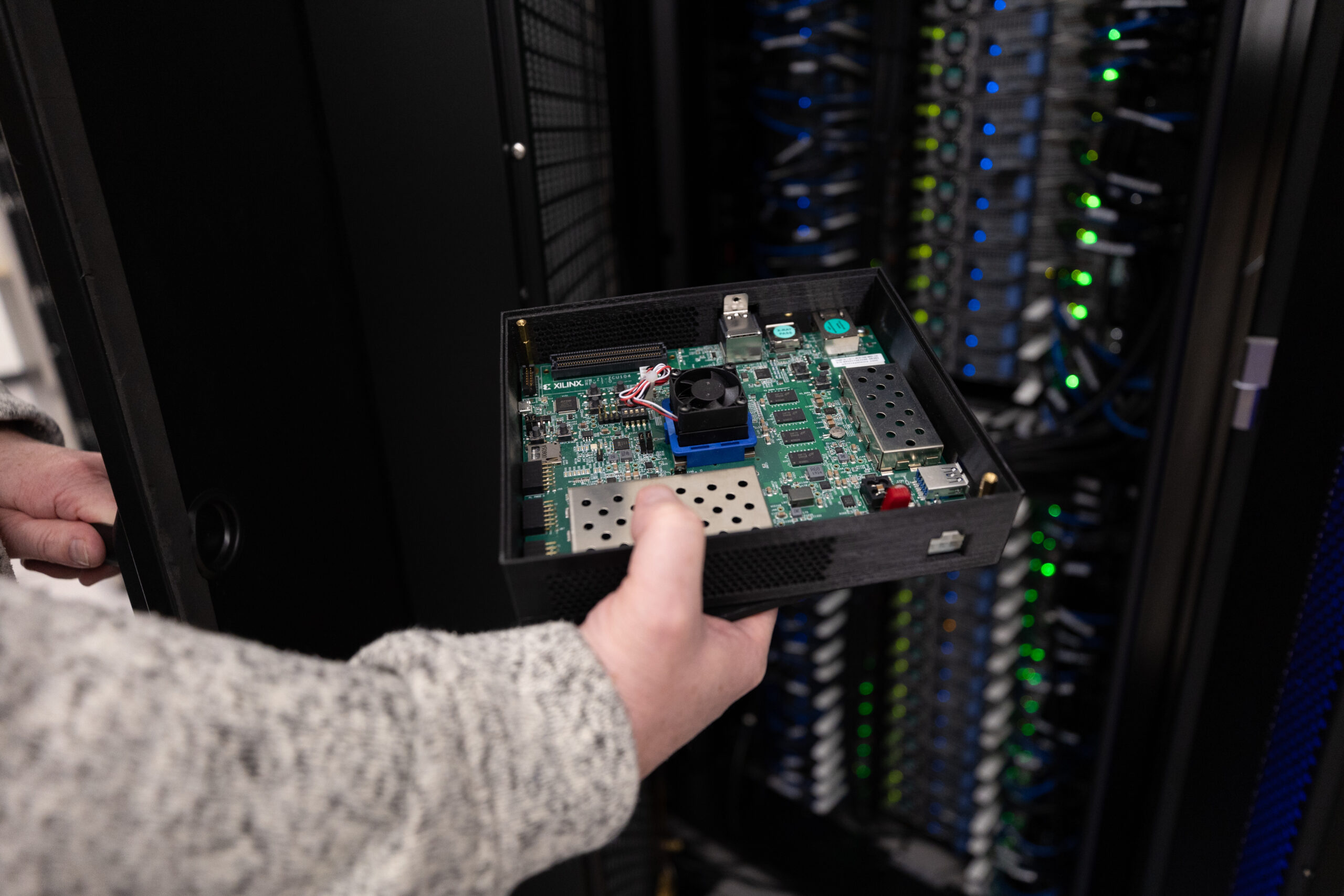
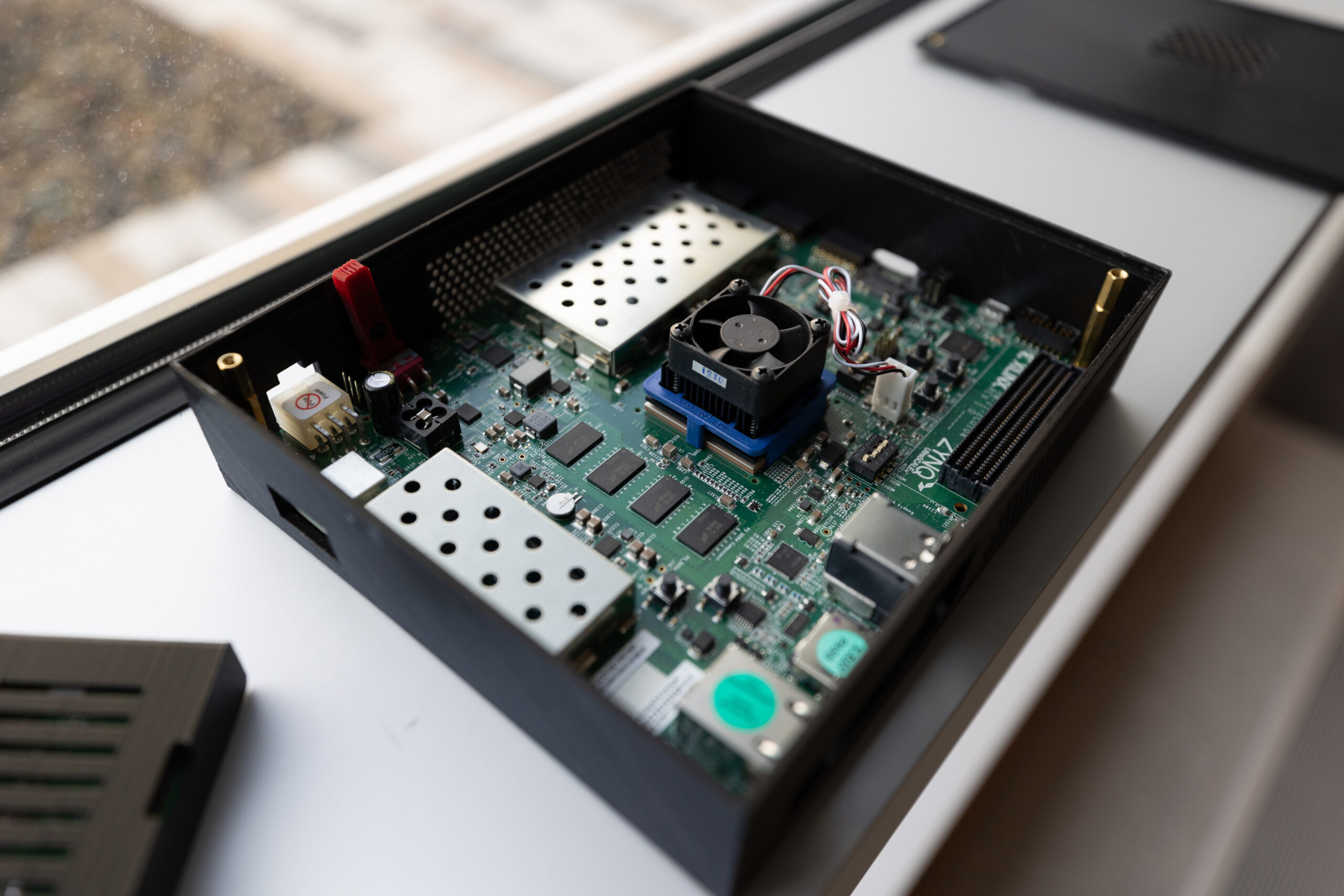
VigilantShield’s ability to prevent digital incursions at the network level required multiple hardware and software innovations to capture malicious behavior that would otherwise be difficult to detect. The technology’s innovations include combining different genres of machine learning to best identify and reduce false alerts, and a programmable logic device that allows the hardware to run faster on very little power and at low cost.
Taking VigilantShield to market
Sub Rosa Ventures (SRV), a security company specializing in sensors that spun out of Cleveland Electric Laboratories, a 100-plus-year-old U.S. based company, sees a future for the technology and plans to make it one of its’ primary focuses in the marketplace, according to SRV President Robert Riegle.
SRV will specifically market VigilantShield to companies and entities that build, manage and secure telecommunication networks.
Partnerships with INL
SRV was motivated to license the technology not just because of VigilantShield novelty, but because past collaborations with INL demonstrated the laboratory’s reputation for quality technologies and research, Riegle said.

“At the end of the day what we like about INL tech is that it’s proven,” Riegle said.
INL Director of Technology Transitions Jason Stolworthy said strategic partnerships and industry engagement are key to moving the lab forward.
“There’s a long list of innovations and technologies that are making a meaningful impact in our communities,” Stolworthy said. “When we pair INL’s innovations with skilled entrepreneurs like Robert Riegle who turn them into cutting-edge commercial products, our lives are improved and America strengthens its global technological leadership.”