Land Stewardship
Land Stewardship involves managing ecosystems on the INL Site through planning, assessment, restoration, and rehabilitation activities.
Areas where the DOE-ID is actively employing land stewardship activities include wildland fire protection planning, management, and recovery, restoration and revegetation, weed management and ecological support for National Environmental Policy Act.
Fire Protection Planning, Management and Recovery
The INL Fire Department provides wildland fire suppression services on the rangeland within the Site boundary as well as a 5-mile buffer outside of the INL Site boundary. The Fire Department employs pre-incident strategies, such as identifying special hazards, mitigation procedures and mapping necessary to respond to fires. DOE-ID maintains mutual aid agreements with regional agencies to help respond to high-challenge wildland fires.
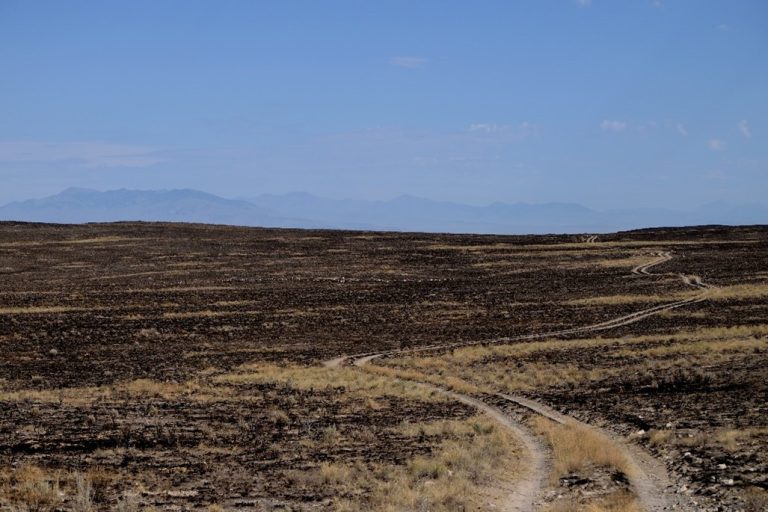

A balanced fire management approach has been adopted to ensure the protection of improved laboratory assets in a manner that minimizes effects on natural, cultural and biological resources. Battelle Energy Alliance, the contractor that manages INL for the Department of Energy, has established a Wildland Fire Management Committee to review seasonal fuel management activities and the potential impact of all fires greater than 40.5 hectares (100 acres).
Revegetation for Soil Stabilization
Revegetation with native species is required on the INL Site for activities that disturb or remove soil and vegetation where the area will not be physically stabilized and maintained as sterile. These areas are left exposed and vulnerable to erosion and invasive or noxious weed infestation. Areas requiring revegetation are evaluated for appropriate revegetation methods based on site conditions and disturbance size.
The baseline conditions of these areas are characterized prior to disturbance, partly to assess the native species present. The native species observed inform an appropriate seed mix to use during revegetation efforts following the disturbance. Revegetation strategies on the INL Site include but are not limited to hand broadcasting seed, seedbed preparation, soil augmentation, drill seeding and planting nursery stock.
Sagebrush Habitat Restoration
Sagebrush habitat restoration on the INL Site is conducted in response to DOE-ID’s goal of no net loss of sagebrush. The potential to lose sagebrush habitat on the INL Site occurs in either wildland fire or infrastructure expansion. INL implements multiple best management practices to minimize current and potential sagebrush habitat loss. The lab also carries out a compensatory sagebrush mitigation strategy for projects that must remove sagebrush habitat.

Sagebrush habitat restoration has been conducted using containerized sagebrush seedlings and aerially applying sagebrush seed. Due to the semiarid nature of the local ecosystem, INL has found that planting sagebrush seedlings results in higher survivorship than trying to establish sagebrush from seed, but continued efforts are exploring ways to improve both future seedings and plantings.
Plants
During the establishment of INL Site research facilities in the 1950s, the Atomic Energy Commission required the flora and fauna to be monitored. Plant specimen collections were made during field surveys and founded the Idaho National Laboratory herbarium. The herbarium contributes to the knowledge of species historically present across the Site. Currently, over 450 plant species occur on the Site, many of which represent the natural sagebrush steppe ecosystem.
Weed Management
Battelle Energy Alliance, the contractor that manages INL for the Department of Energy, maintains and funds a noxious and invasive weed management program to address requirements of federal agencies described in Executive Order 13112, “Invasive Species,” as amended by Executive Order 13751, “Safeguarding the Nation from the Impacts of Invasive Species.” The noxious and invasive weed species management program on the INL Site fulfills these requirements by first ensuring that preventing the introduction, establishment and spread of invasive species is prioritized during all activities. This is partly carried out by discouraging unnecessary actions that can create spreading vectors or new introductions.
Where noxious weeds and invasive species are present on the INL Site, they are treated and managed appropriately by implementing Integrated Pest Management principals. These principles are intended to ensure the treatment method that poses the least risk to the environment and human health is prioritized and implemented as appropriate.
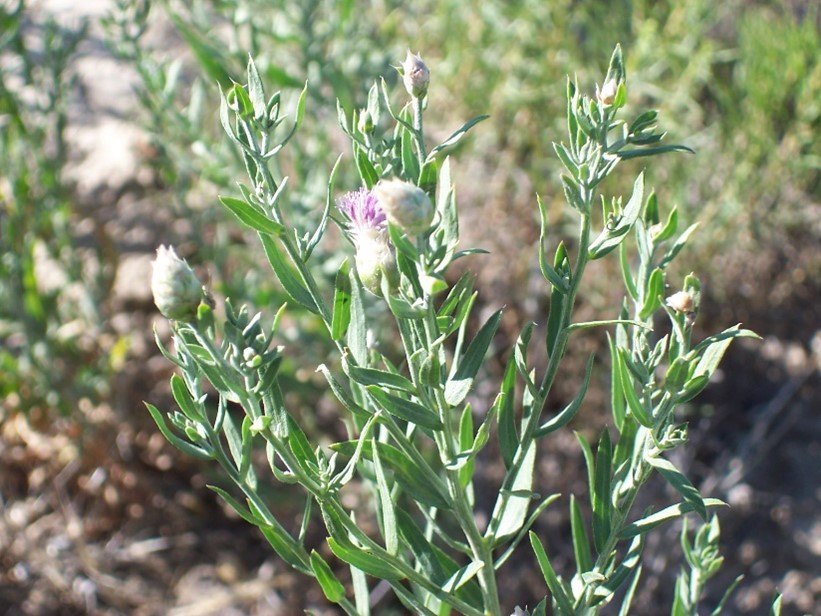


Ecological Support for National Environmental Policy Act
The Natural Resources Group supports planning and decision-making under the National Environmental Policy Act in ecological support documents by identifying and evaluating potential impacts to natural resources for each proposed INL project. These ecological support documents are developed to support environmental assessments and environmental impact statements by providing data on the presence or absence of certain natural resources in the vicinity of a proposed INL project.