Advanced Test Reactor
INL’s Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is the world’s premier nuclear test reactor. It provides unmatched, national priority nuclear fuel and materials testing capabilities for military, federal, university and industry partners and customers.
INL’s nuclear research capabilities rely heavily on ATR, located at the ATR Complex on the INL Site, 47 miles west of Idaho Falls.
As the national laboratory for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy (DOE-NE), INL serves a key role in U.S. nuclear energy research initiatives and programs, such as the National Reactor Innovation Center.
How is ATR Used?
ATR’s capabilities and infrastructure are accessible through various programs that support the U.S. and international nuclear research efforts. ATR is the only U.S. research reactor capable of providing large-volume, high-flux thermal neutron irradiation in a prototype environment. The reactor’s singular design makes it possible to study the effects of intense neutron and gamma radiation on reactor materials and fuels.
Reactor Type
ATR is a one-of-a-kind pressurized water test reactor. As a test reactor, it operates at very low pressures and temperatures compared to a large commercial nuclear power plant. Instead of heat, the main product of a test reactor is the neutrons it produces. ATR uses a beryllium reflector to help concentrate neutrons in the core, where they are needed for fuels and materials testing.
Design Features
ATR’s unique cloverleaf core design allows the reactor’s corner lobes to be operated at different power levels, making it possible to conduct multiple simultaneous experiments under different testing conditions. Other key features that make ATR unique are listed in the fact sheets on this page.
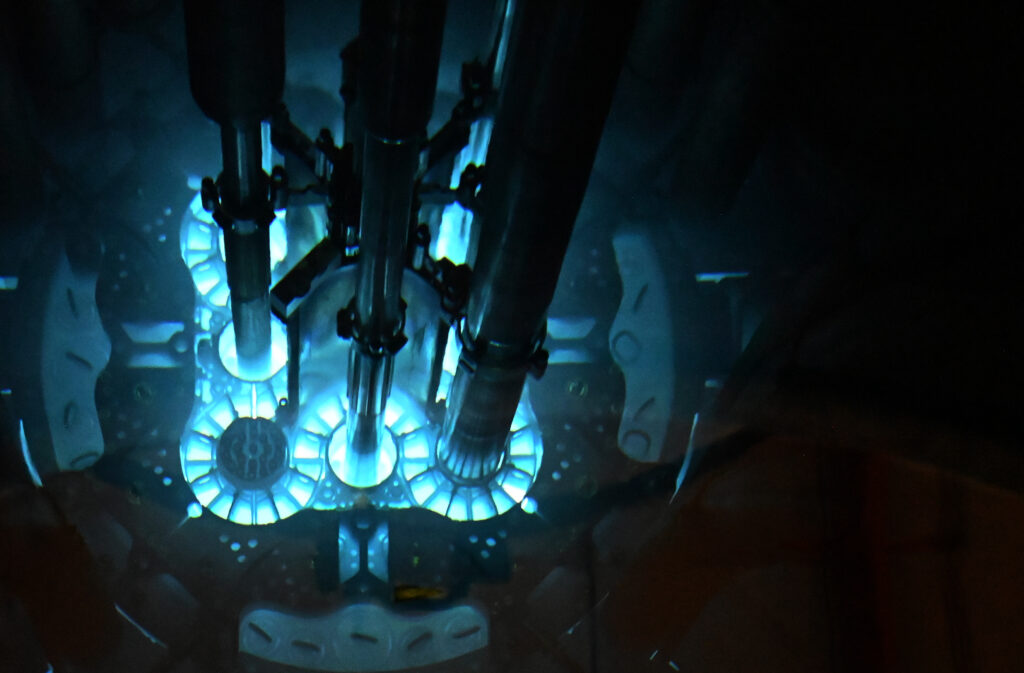
ATR’s distinctive cloverleaf core sets it apart from every other test and research reactor in the world, and is the key to its world-leading capabilities.
Research and Capabilities
National Security
Over the years, ATR has provided vital irradiation testing capability supporting the U.S. Navy’s nuclear propulsion program. The Navy remains a key customer of ATR and testing has contributed to the exceptional operational performance of the nuclear-powered fleet.
Nuclear Energy
Experiments conducted at ATR provide a critical look at reactor components and systems. Testing at ATR supports reactor research around the world to extend the life of current nuclear power plants, develop designs for advanced reactors, and test new types of stronger nuclear fuels that reduce waste generation and proliferation risks.
Collaborative Research
ATR’s capabilities are an essential part of efforts to support nuclear energy research and development in the U.S. and around the world. ATR capabilities are accessible to universities, industry and international partners through DOE’s Nuclear Science User Facilities, the Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear, and the National Reactor Innovation Center, as well as other research partnerships. ATR’s capabilities are also key to INL’s certification to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) International Center of Excellence based on Research Reactors (ICERR) standard. These capabilities are summarized in the ATR User Guide.
Isotope Production
ATR is the only U.S. source of the valuable medical grade cobalt-60 isotope needed for “gamma knife” therapy used to treat brain tumors, and produces plutonium-238 for NASA’s deep space exploration missions.
Renewing ATR Sustains Peak Performance
ATR employs a unique design in which key internal components can be completely replaced during a core overhaul every 10 years on average to enable long-term operations. This overhaul is called a Core Internals Changeout. ATR recently underwent its sixth core overhaul during 2021-2022.
Numerous other upgrades and improvements have been done since ATR entered service in 1967. The Department of Energy is continuing to invest in infrastructure upgrades on the reactor and key plant facilities to ensure ATR can continue to serve the nation’s needs for decades to come.
This planning includes the procurement and availability of critical spare parts, including one-of-a-kind components such as core internal components and beryllium reflectors. Planning also addresses staffing requirements and identifies the funding, schedule and prioritization for replacing key components and systems.

2017 was a banner year for INL’s Advanced Test Reactor, marking 50 years of operation for one of the most innovative, flexible and durable scientific research tools ever built. The reactor was designed by Deslonde de Boisblanc in 1959.
At its groundbreaking ceremony in 1961, Idaho Gov. Robert E. Smylie said the $40 million project was the largest construction project in the history of the state. It began operating in 1967. Celebrations to honor the reactor’s 50-year anniversary were held in June 2017. ATR leadership and dignitaries across the state recognized the occasion.
